Menu
Free Consultation
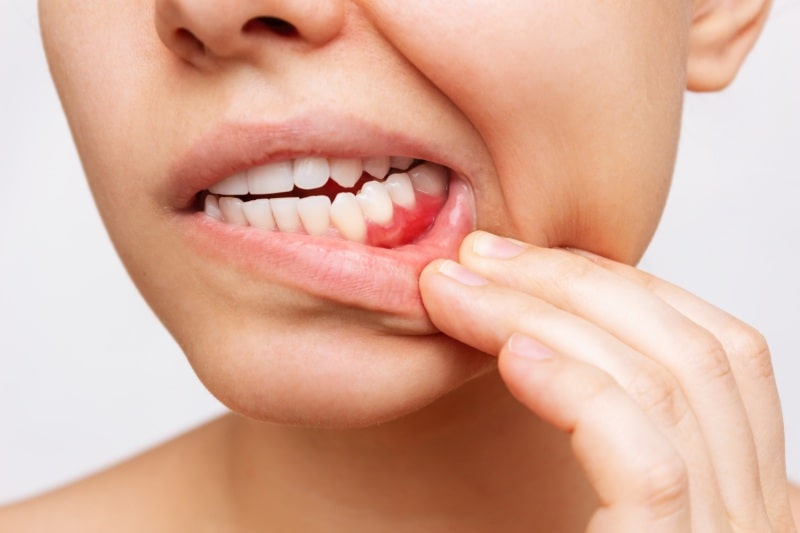
Approximately 70% of tooth loss in adults is caused by problems with the gums. Periodontology is the branch of science that deals with the surrounding tissues of the teeth. Inflammatory diseases that occur in these tissues for various reasons are called periodontal diseases or gum diseases.
Gum diseases, a health problem characterized by inflammation and damage to the gums, are extremely common. If left untreated, gum diseases, which are usually caused by bacterial infections caused by plaque and tartar accumulation, can cause bad breath, bleeding, loose teeth and even tooth loss. Since gum disease usually progresses painlessly, it is recognized in the later stages in most patients.
The gums, the jawbone and the periodontal fibers that connect the teeth and the jawbone are the tissues around the teeth. The types of periodontal diseases are defined depending on which of the surrounding tissues is affected by the infection. The most common gingival diseases include gingivitis, chronic periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, periodontitis as a symptom of systemic diseases, necrotizing periodontal diseases, periodontitis associated with endodontic lesions and abscesses of the periodontium.
Gingivitis is when the gums are affected by infection. The gums may appear red and swollen and may bleed and have bad breath. If gingivitis is left untreated, the infection can progress and lead to the development of periodontitis.
Periodontitis is when the periodontal fibers and jawbone are affected by the infection in addition to the gums. A so-called "periodontal space" forms between the tooth and gum and bacteria can easily settle in this space. The presence of a periodontal pocket causes the infection to settle and the disease to progress easily. As the disease progresses, tissue loss occurs and the teeth begin to wobble. As a result, teeth may need to be extracted.
Gum diseases are infectious diseases that affect the tissues around the teeth. Even people with no decay in their teeth may experience tooth loss due to gum disease. Gum diseases can be seen in all age groups. However, since it usually proceeds painlessly, its symptoms are recognized late and it may be late to consult a dentist. For this reason, routine dental examinations can be beneficial in the prevention and early diagnosis of gum diseases.
The most common symptoms of gum diseases are listed below:
Gum diseases can usually be treated with non-surgical approaches in the early period. In the initial periodontal treatment, tooth and root surface cleaning is performed. The patient is informed about how to maintain oral hygiene. Occlusion is checked. Retention areas such as cavities and wisdom teeth that facilitate the accumulation of food debris and microorganisms are removed to reduce or eliminate inflammation in the gums and remove microorganisms that cause gingivitis. After the course of treatment, the gum adapts and shrinks back to the tooth and the pocket of tissue is eliminated.
In more advanced cases, a surgical procedure is required. Tartar is removed from the periodontal pockets surrounding the teeth. This results in a smooth root surface and a gingival form that is easier for the patient to clean. Surgical interventions may include subgingival curettage, gingivectomy, gingivoplasty and flap operation.
Gum diseases can be caused by many different reasons. The first among these is microbial dental plaque. In case of insufficient oral hygiene, food residues that cannot be cleaned and bacteria from saliva combine to form a sticky layer. Microbial dental plaque can cause gum diseases by destroying the tissues around the teeth.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menopause, puberty and menstruation can disrupt the structure of gum cells and cause gingivitis. Stress can weaken the immune system and reduce the gums' resistance to infections. Malnutrition can negatively affect gum health. In addition, systematic diseases such as smoking and diabetes can also be listed among the causes of gum diseases.
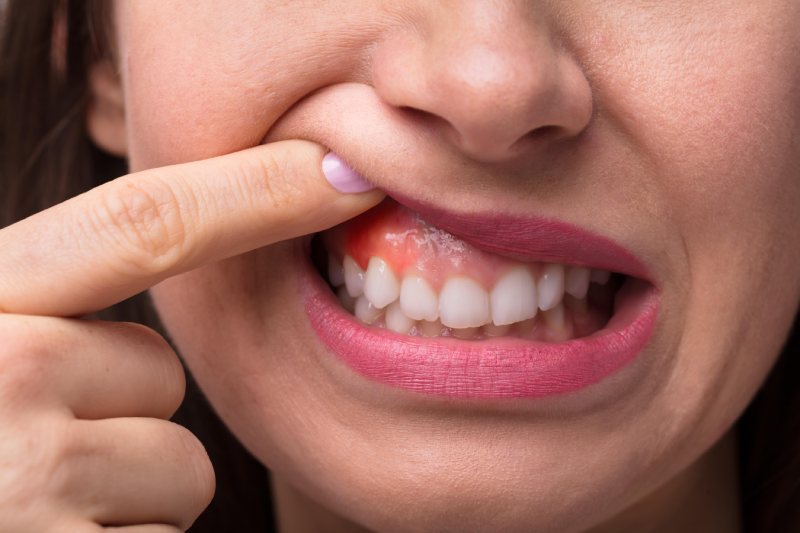
The most important factor causing gum diseases is the formation of bacterial plaque. In addition, consumption of alcohol, cigarettes and other tobacco products, side effects of certain medications, malnutrition and stress can cause tooth and gum diseases. Eliminating these causes is the first step to be taken to prevent tooth and gum diseases.
Smoking: In addition to all the known harms to the human body, smoking is an extremely harmful habit for oral and dental health. Smoking triggers oral and dental diseases, in other words periodontal diseases. Due to the heat of the cigarette, inflammation in the mouth can sometimes be concealed. In this case, the cigarette provides favorable conditions for the inflammation to hide. In such cases, the inflammation cannot be recognized unless it gives any symptoms.
Pregnancy and puberty: Periods such as pregnancy and puberty, when almost all hormones in the body change, also affect the mouth and teeth. Especially during these periods, a complete oral and dental care routine should be followed, teeth should be brushed and flossed regularly to prevent plaque build-up.
Diseases that affect the general health of the body: Diseases that target the body's defense system, such as diabetes, leukemia and AIDS, can impair the health of the gums. People with such health problems are very vulnerable to the development of infection. In addition, infection in the gums causes severe pain. It is also extremely difficult to control.
Various medications used: Some medications, such as anti-depressants and blood pressure medications, can adversely affect the oral tissues. In such cases, the gums can also suffer adverse effects.
Stress: Stress, which causes various damages in almost all parts of our body, can also have negative effects on oral and dental health. In addition, the process of fighting infection can become difficult due to stress.
Malnutrition: As a result of malnutrition, which weakens the immune system, the body can become vulnerable to infections and have difficulty fighting infections. Since oral and dental diseases are extremely serious infections, gingivitis can be exacerbated if malnutrition continues. In advanced stages, there may be undesirable situations such as tooth loss.
If gum diseases are not recognized or their treatment is neglected, very serious consequences can be faced. Gum diseases usually start with mild symptoms in the first stage, and more serious problems may arise over time. If gum diseases are not recognized or treated, the consequences that may be encountered can be listed as follows:
There is a strong relationship between gum disease and general health. Therefore, oral and dental health directly affects general health. According to research, gum disease can increase inflammation in the body, which in turn can increase the risk of heart disease. In addition, diabetes can facilitate the development of gum disease, and poor oral health can make it difficult to control diabetes. Gum disease is associated with an increased amount of bacteria in the mouth, which can lead to an increased risk of respiratory infections.
