Introduction
Healthy gums are essential for a strong, beautiful smile and long-lasting oral health. But many people notice their gums pulling back, making teeth look longer and exposing sensitive roots. This condition, known as receding gums, is not just a cosmetic issue—it can also signal gum disease, bone loss, or other oral health problems.
If you’ve ever wondered, “Why are my gums receding?”, “How to fix receding gums?”, or even read stories like “I healed my receding gums”, this article will guide you through everything you need to know. From receding gums treatment options to how to stop receding gums from progressing, we’ll cover the causes, prevention, and both natural and professional solutions.
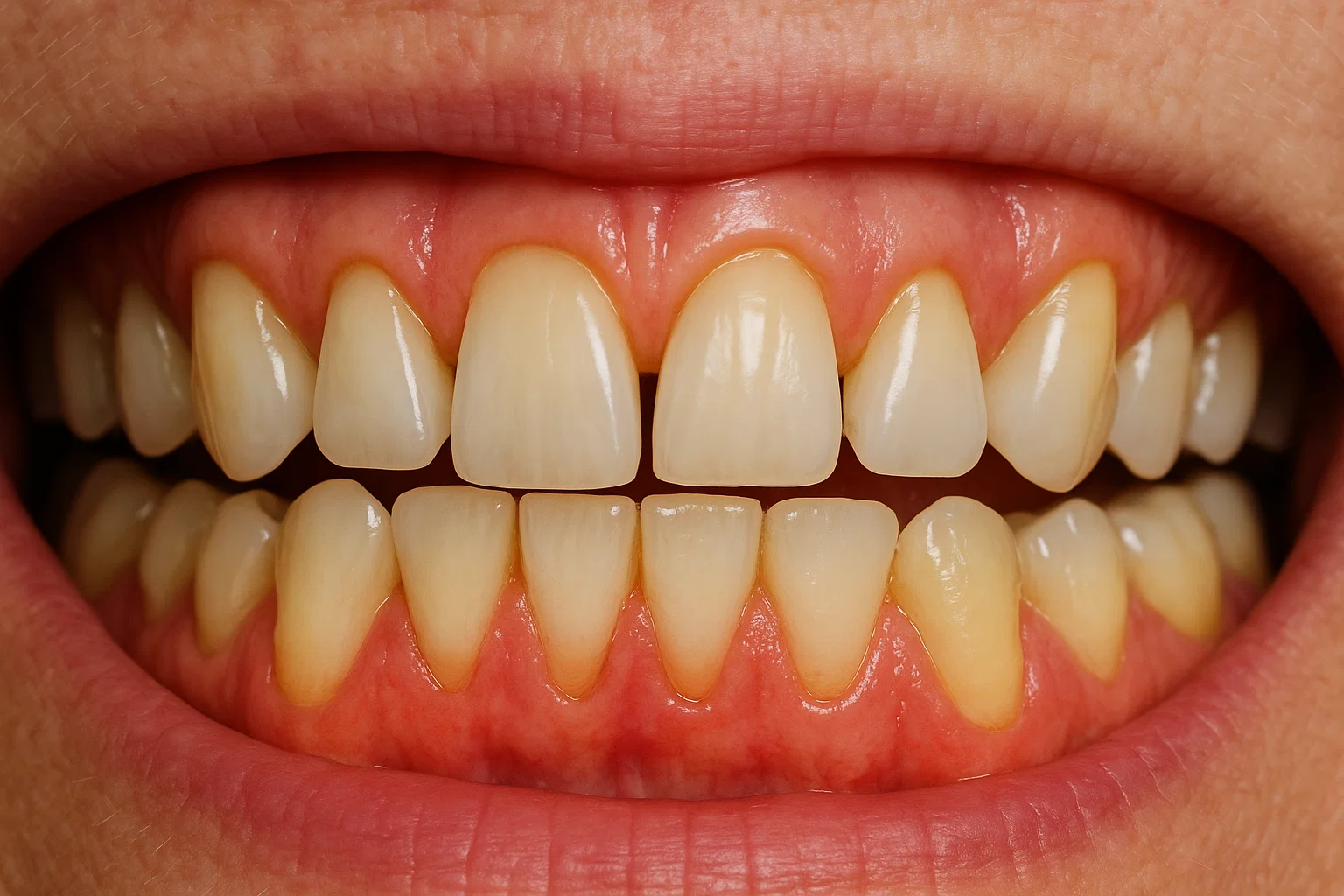
What Are Receding Gums?
Receding gums occur when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth gradually wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This can create gaps between the teeth and gums, where bacteria can accumulate, leading to further damage if left untreated.
Key Characteristics
- Teeth appear longer than normal
- Roots may become visible
- Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods
- Inflammation or bleeding when brushing
- Pockets forming between teeth and gums
Extra Clinical Detail: Stages of Gum Recession
- Mild recession – 1–2 mm of gum loss, often with mild sensitivity
- Moderate recession – 3–4 mm of gum loss, visible tooth root, possible gum inflammation
- Severe recession – More than 5 mm of gum loss, tooth mobility, risk of bone loss
What Causes Receding Gums?
Understanding what causes receding gums helps in finding the right treatment and preventing future damage.
1. Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
- The most common cause of receding gums
- Bacterial infection damages gum tissue and bone
- Leads to inflammation, bleeding, and eventual tooth loss if untreated
2. Aggressive Tooth Brushing
- Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too forcefully can erode enamel and gum tissue
3. Poor Oral Hygiene
- Plaque buildup hardens into tartar, irritating gums and causing them to recede
4. Genetics
- Some people are naturally predisposed to thinner gum tissue
5. Hormonal Changes
- Pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal fluctuations can make gums more sensitive and prone to recession
6. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
- Puts excessive force on teeth, leading to gum tissue breakdown
7. Misaligned Teeth or Bite Issues
- Uneven pressure during chewing can stress gums and bone
8. Tobacco Use
- Smoking and chewing tobacco reduce blood flow to gums and increase risk of gum disease
🧾 Case Example: A 45-year-old smoker with poorly controlled diabetes presented with sensitive, elongated teeth and bleeding gums. Diagnosis: moderate receding gums caused by combined periodontal disease, smoking, and systemic factors.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Recognizing symptoms of receding gums early is crucial for effective treatment.
- Tooth sensitivity to temperature changes
- Teeth looking longer than before
- Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing
- Loose teeth in advanced cases
- Bad breath (halitosis) from bacteria buildup
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
Additional Symptoms to Watch For
- Changes in bite alignment (teeth may not fit together properly)
- Spaces between teeth widening due to gum loss
- Frequent infections or abscesses around the gum line
- Metallic taste in the mouth (can indicate infection)
Can Receding Gums Be Reversed?
A common question is: “Can receding gums be reversed?”
- Early stages: Gum irritation without significant tissue loss can often be reversed with improved oral hygiene and professional cleaning.
- Moderate recession: Once gum tissue has been lost, it cannot grow back naturally. However, treatments can regenerate supporting structures or restore gum coverage using grafting.
- Severe cases: Advanced gum recession may require surgical procedures for repair.
🦷 Real Patient Insight: Many patients share experiences online saying, “I healed my receding gums.” What they usually mean is that they improved gum health, reduced inflammation, and stopped further gum loss—not that the gums fully regrew naturally.
How to Stop Receding Gums
Preventing further gum loss is just as important as treating existing damage. Here’s how to stop receding gums from getting worse:
- Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Switch to SLS-free toothpaste (gentler on gums)
- Quit smoking or chewing tobacco
- Treat teeth grinding with a nightguard
- Correct bite alignment if uneven pressure is present
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for professional cleanings
🔑 Tip: Use the “modified Bass technique” for brushing—hold the brush at a 45° angle to the gumline and make gentle circular motions.
How to Fix Receding Gums: Treatment Options
If you’re asking “how to fix receding gums”, there are both non-surgical and surgical receding gums treatments available.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Professional Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing): Removes tartar and bacteria below the gumline
- Antibiotic Rinses or Gels: Reduce bacterial infection and inflammation
- Desensitizing Agents: Relieve sensitivity from exposed roots
- Laser therapy: May reduce bacteria and promote healing with minimal discomfort
Surgical Treatments
- Gum Grafting Surgery: Tissue from your palate or donor source is grafted to cover exposed roots
- Pinhole Surgical Technique: A minimally invasive method to reposition gum tissue without sutures
- Regenerative Procedures: Use membranes, proteins, or grafts to regenerate lost bone and tissue
Healing Timeline
- Initial improvement: within 1–2 weeks after non-surgical cleaning
- Graft healing: 4–6 weeks for full recovery
- Long-term stability: requires excellent home care and regular dental monitoring
Natural Approaches and Home Remedies
While they cannot replace professional treatment, natural remedies can support gum health:
- Oil Pulling (Coconut or Sesame Oil): May reduce bacteria and inflammation
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants that support gum health
- Aloe Vera Gel: Anti-inflammatory and soothing for irritated gums
- Turmeric Paste: Natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial benefits
- Vitamin C & Omega-3 Supplements: Promote healing and strengthen gum tissue
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water keeps gums moist and flushes bacteria
- Healthy diet: Leafy greens, nuts, salmon, and citrus (in moderation to prevent acid damage) support gum health
The Link Between Receding Gums and Other Health Issues
Research shows that gum health is connected to overall health:
- Heart disease: Chronic inflammation may increase cardiovascular risk
- Diabetes: Gum disease can worsen blood sugar control, and vice versa
- Pregnancy complications: Gum problems linked to preterm birth or low birth weight
- Respiratory infections: Oral bacteria may spread to lungs in vulnerable patients
🧠 Advanced Insight: Gum disease bacteria (Porphyromonas gingivalis) has been linked to systemic inflammation and even conditions like Alzheimer’s disease in some studies.
Living with Receding Gums: Patient Stories
Case Study 1: “I Healed My Receding Gums”
A 32-year-old patient reported gum bleeding and sensitivity. By switching to a soft-bristle brush, flossing daily, quitting soda, and using an antibacterial mouth rinse, she noticed her gums stopped bleeding, and sensitivity decreased. While the gums didn’t regrow, the condition stabilized.
Case Study 2: Surgical Success
A 50-year-old patient with severe gum recession underwent connective tissue grafting. After 6 weeks, gum coverage improved, sensitivity reduced significantly, and the patient reported increased confidence in smiling.
FAQs About Receding Gums
How to fix receding gums?
Professional treatments like scaling, root planing, and gum grafting surgery are effective. Home care helps prevent further progression.
How to stop receding gums?
Brush gently, floss daily, use a soft toothbrush, avoid smoking, and treat bruxism. Regular dental checkups are essential.
What causes receding gums?
The most common causes are gum disease, aggressive brushing, genetics, poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, and teeth grinding.
Why are my gums receding?
Gums recede due to plaque buildup, periodontal disease, aging, or mechanical trauma such as harsh brushing.
Can receding gums be reversed?
Early gum irritation can be reversed with proper care, but lost gum tissue does not regrow naturally. Surgical grafting may restore coverage.
Conclusion
Receding gums are a common but serious dental issue. While you may come across personal accounts like “I healed my receding gums”, it’s important to understand that natural remedies and home care can improve gum health and stop receding gums from worsening, but they cannot replace lost gum tissue.
For true restoration, professional receding gums treatment—such as grafting or regenerative procedures—is often necessary. Still, with consistent oral hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and timely dental care, you can prevent further gum loss and maintain a healthy, confident smile.
✅ Final Word: Don’t wait until your teeth feel loose or painful. If you notice any symptoms of receding gums, seek professional evaluation early. Prevention and timely treatment are the keys to saving your gums and protecting your natural teeth for life.