Everything You Need to Know About the Best and Safest Treatments for Osteoporosis
Introduction: Understanding Osteoporosis and the Need for Timely Treatment
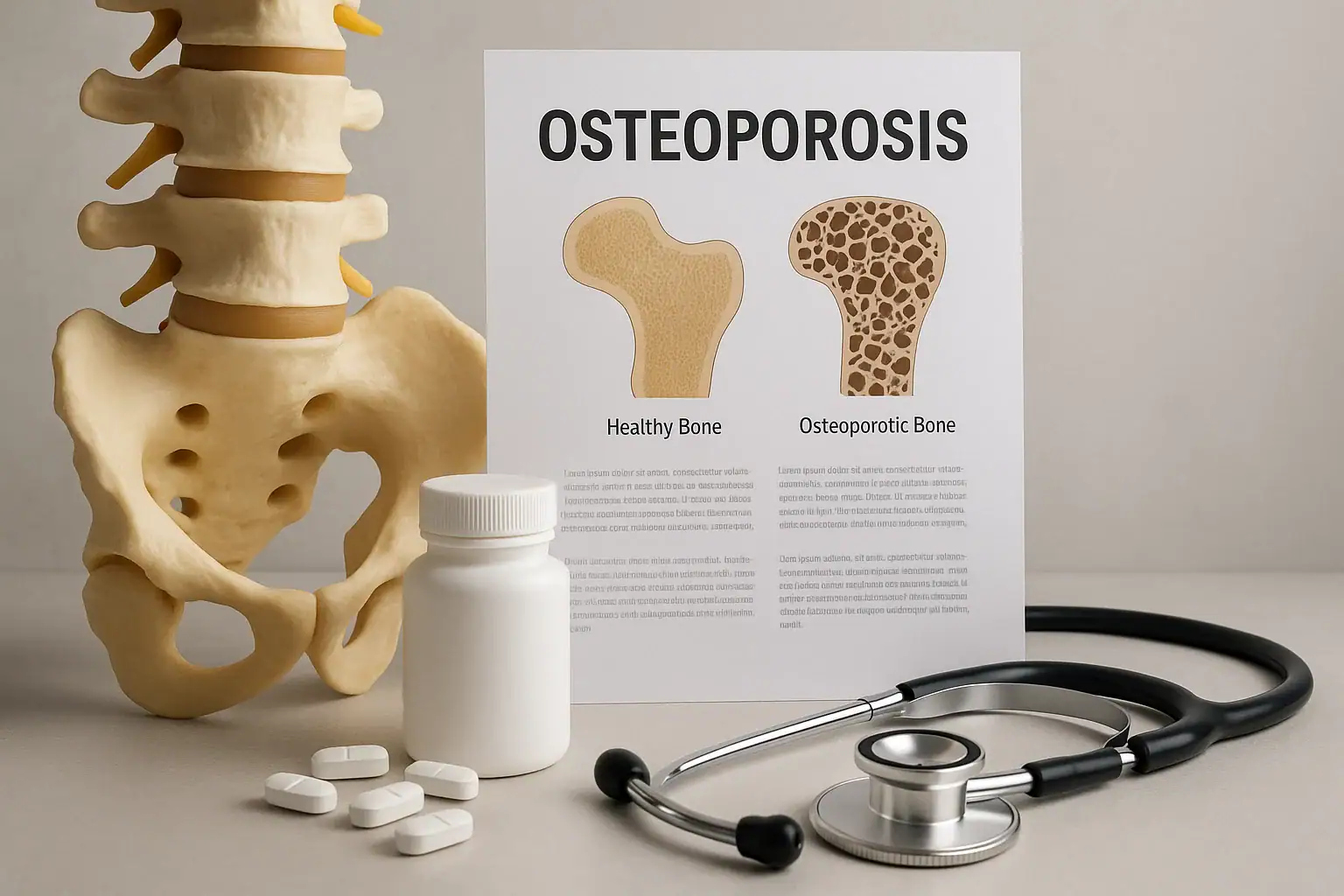
Osteoporosis is a chronic bone disease characterized by reduced bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. Often called the “silent disease,” osteoporosis can progress without symptoms until a fracture occurs. Effective and timely osteoporosis treatment is critical to preventing complications and improving quality of life.
In this article, we’ll explore treatments for osteoporosis, including medication options, lifestyle interventions, dietary changes, and cutting-edge therapies available in 2025. We’ll also answer top FAQs such as what is the best and safest treatment for osteoporosis?
What Is the Treatment for Osteoporosis?
Standard Goals of Osteoporosis Treatment
The primary objectives of treating osteoporosis are:
- Reducing the risk of fractures
- Increasing or stabilizing bone density
- Improving bone quality
- Alleviating pain associated with fractures
A comprehensive treatment for osteoporosis typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, nutritional support, and physical therapy.
Types of Osteoporosis Treatments
1. Bisphosphonates – First-Line Therapy
Bisphosphonates are among the most common osteoporosis treatments and include:
- Alendronate (Fosamax)
- Risedronate (Actonel)
- Ibandronate (Boniva)
- Zoledronic acid (Reclast)
They work by slowing down bone resorption, helping bones remain dense and strong. Pros: Proven to reduce fracture risk
Cons: Can cause gastrointestinal issues and rare side effects like jaw osteonecrosis
2. Denosumab (Prolia) – Monoclonal Antibody Option
Denosumab is an injection given twice a year and is ideal for patients who can’t tolerate bisphosphonates. Pros: Increases bone density in spine and hips
Cons: Bone loss may rapidly resume after stopping the drug
3. Parathyroid Hormone Analogs – Stimulating New Bone Growth
Medications like teriparatide (Forteo) and abaloparatide (Tymlos) mimic the natural hormone to stimulate bone formation. Pros: Excellent for severe osteoporosis
Cons: Use is typically limited to two years
4. Romosozumab (Evenity) – Dual Action Treatment
This newer treatment both builds new bone and decreases resorption. Pros: Quick results with monthly injections
Cons: Limited to a 12-month course; may carry cardiovascular risk
5. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
In postmenopausal women, HRT can help maintain bone mass. However, it comes with significant risks such as breast cancer and cardiovascular disease, so it's not a first-line treatment.
Nutritional Approaches to Osteoporosis Treatment
Importance of Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium is vital for bone strength, while Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium effectively.
- Calcium requirement: 1000–1200 mg/day
- Vitamin D requirement: 600–800 IU/day
These can be obtained through diet (milk, leafy greens, almonds) or supplements.
Bone-Boosting Foods
Include foods high in:
- Magnesium (avocados, nuts)
- Vitamin K (broccoli, kale)
- Protein (lean meats, legumes)
Avoid excess alcohol, caffeine, and sodium, which can weaken bones.
Exercise and Lifestyle Changes
Weight-Bearing and Resistance Training
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective treatments for osteoporosis that doesn't involve medication. Recommended activities:
- Walking or light jogging
- Resistance band workouts
- Yoga for balance and posture
Important: Avoid high-impact or twisting motions that could cause fractures.
Quitting Smoking and Limiting Alcohol
Both smoking and excessive alcohol use are linked to decreased bone density. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake to one drink per day can significantly help with bone health.
Osteoporosis Risk Factors: Who Is Most at Risk?
Major Risk Factors:
- Postmenopausal women, especially over age 50
- Family history of osteoporosis or fractures
- Low body weight or BMI < 19
- Sedentary lifestyle or prolonged immobility
- Long-term steroid use (e.g., prednisone)
- Chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, or kidney disease
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Low calcium/Vitamin D intake during youth
How Is Osteoporosis Diagnosed?
Common Diagnostic Methods:
- DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scan – the gold standard
- FRAX Score – calculates your 10-year probability of fracture
- Blood Tests – calcium, vitamin D, thyroid function, bone turnover markers
- X-rays – may reveal fractures or severe bone loss
- Bone turnover markers (BTMs) – monitor treatment effectiveness
Medication Side Effects: What to Expect
Bisphosphonates
- Heartburn
- Difficulty swallowing
- Jaw osteonecrosis (very rare)
- Atypical femoral fractures (rare, long-term use)
Denosumab
- Low calcium (hypocalcemia)
- Skin infections
- Rapid bone loss after stopping
Parathyroid hormone analogs
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Increased calcium levels
Genetic Testing in Osteoporosis Management
Recent advances have made it possible to assess genetic predisposition to osteoporosis through DNA testing.
- Identifies mutations affecting bone metabolism
- Predicts response to specific medications
- May guide personalized treatment strategies
When to See a Specialist
Consider consulting an:
- Endocrinologist
- Rheumatologist
- Orthopedic doctor
- Geriatrician
Long-Term Monitoring and Follow-Up
Follow-up Recommendations:
- Bone density scan every 1–2 years
- Monitoring Vitamin D and calcium levels
- Reassess medications and lifestyle
- Consider drug holidays after 3–5 years under medical advice
Psychological and Emotional Impact of Osteoporosis
Common Emotional Challenges:
- Fear of falling
- Anxiety about fractures
- Depression from reduced independence
- Social withdrawal
Tip: CBT, support groups, and rehab can improve quality of life.
Global Trends in Osteoporosis Treatment (2025)
Highlights:
- Japan & Scandinavia: Focus on preventive screening
- USA & Canada: Better access to injectables
- Europe: AI tools in bone screening
- Middle East & Asia: Awareness and telemedicine expansion
Future of Osteoporosis Treatment
Emerging Therapies:
- Anabolic agents
- Gene therapy
- Smart implants
- Bone regeneration scaffolds
What Is the Best and Safest Treatment for Osteoporosis in 2025?
No universal answer exists. The best and safest treatment for osteoporosis depends on:
- Age and gender
- Severity of bone loss
- Tolerance to medications
- Comorbidities
- Fracture risk
Typical 2025 combination:
- Bisphosphonates
- Calcium + Vitamin D
- Lifestyle modifications
- Romosozumab (severe cases)
- Denosumab (renal issues)
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the treatment for osteoporosis?
Medications, supplements, and lifestyle changes.
What is the best and safest treatment for osteoporosis in 2025?
Bisphosphonates, romosozumab, and personalized plans are preferred.
What are the treatments for osteoporosis?
Medications, hormone therapy, diet, exercise, and more.
What osteoporosis treatments are covered by insurance?
Most standard drugs and supplements; newer drugs may need prior approval.
How long do osteoporosis treatments take to show results?
Improvements typically within 6–12 months; fracture reduction may occur sooner.
Final Words: Taking Charge of Bone Health
Osteoporosis is manageable with early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. In 2025, innovative options make it easier than ever to live a full, fracture-free life.