Menu
Free Consultation
Did you know that women tend to smile more frequently and expansively than men during social interactions, which can significantly shape first impressions and perceptions of approachability? In fact, research shows that men often rate women as more attractive based on a smiling first impression, while proud or neutral expressions rank lower. This subtle yet powerful difference highlights the fascinating intersection of dental health and gender-specific aesthetics, where feminine dental appearance often emphasizes softness and radiance, and masculine smile aesthetics convey strength and resolve.
At its core, the topic of feminine appearance versus masculine appearance in dental health explores how anatomical, behavioral, and perceptual factors influence our smiles. Men's teeth are typically 10-12% larger and wider than women's, with longer canines and broader incisors contributing to a more rugged look, while women's smaller, narrower teeth and shorter roots promote a delicate, youthful vibe. These variances aren't just cosmetic; they tie into broader oral health patterns. Women generally exhibit better hygiene habits, brushing twice daily about 8% more often than men and visiting dentists more regularly, yet they're more prone to cavities due to hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. Conversely, men face higher risks of gum disease (56% prevalence versus 38% in women) and oral cancer, often linked to poorer self-care and lifestyle factors like smoking.
Understanding these gender differences in oral health is crucial for aesthetic dentistry, as it empowers individuals to enhance their self-confidence and overall well-being. A well-aligned, healthy smile not only boosts social and professional interactions but also reflects underlying health. Poor dental care can erode perceived femininity through staining or recession, or diminish masculinity via uneven wear. This comprehensive guide delves into anatomical distinctions, key aesthetic features for feminine and masculine smiles, health implications, tailored procedures, and maintenance tips to help you achieve an optimized, gender-aligned dental appearance that stands out.
Human dental anatomy exhibits notable sexual dimorphism, with men's teeth generally being larger, wider, and longer than women's. Studies indicate that male tooth crowns are approximately 10-12% larger overall, attributed to a longer period of amelogenesis and greater dentine volume in males. For instance, central incisors in men are about 8-10% wider, and canines are longer by 3-7%, contributing to a more robust appearance. In contrast, women's teeth are smaller and narrower, with shorter roots. Mandibular incisors, for example, can be up to 20% shorter, promoting a more delicate structure. Interestingly, while males have more dentine, females often exhibit relatively thicker enamel, though overall tooth size favors males due to body bulk differences. These variances extend to dental arches: males typically have wider arches, while females show narrower configurations.
Facial shape plays a crucial role in how these dental features are perceived, correlating with gender-specific aesthetics. Oval faces predominate across genders, but more so in women (53.3%) compared to men (42.5%), while men are more likely to have triangular (40%) or square (26%) shapes, influencing smile dynamics. Triangular or square faces in men enhance the perception of strength when paired with broader teeth, whereas oval shapes in women accentuate softness with narrower incisors.
Perception studies reveal gender-based differences in aesthetic evaluation. Women tend to assign higher scores to dental aesthetics and are more dissatisfied with their own appearance, viewing teeth as key to attractiveness. The smile is often the first facial feature noticed in women, evoking approachability, while eyes may draw initial attention in men. Females report greater satisfaction with their dental appearance overall, yet prioritize smoothness and rounded tooth forms for femininity. Conversely, larger, square teeth bolster masculine ruggedness, aligning with perceptions of authority.
These anatomical and perceptual differences underscore how dental features reinforce gender perceptions, guiding aesthetic dentistry toward personalized enhancements that amplify natural traits without stereotyping.
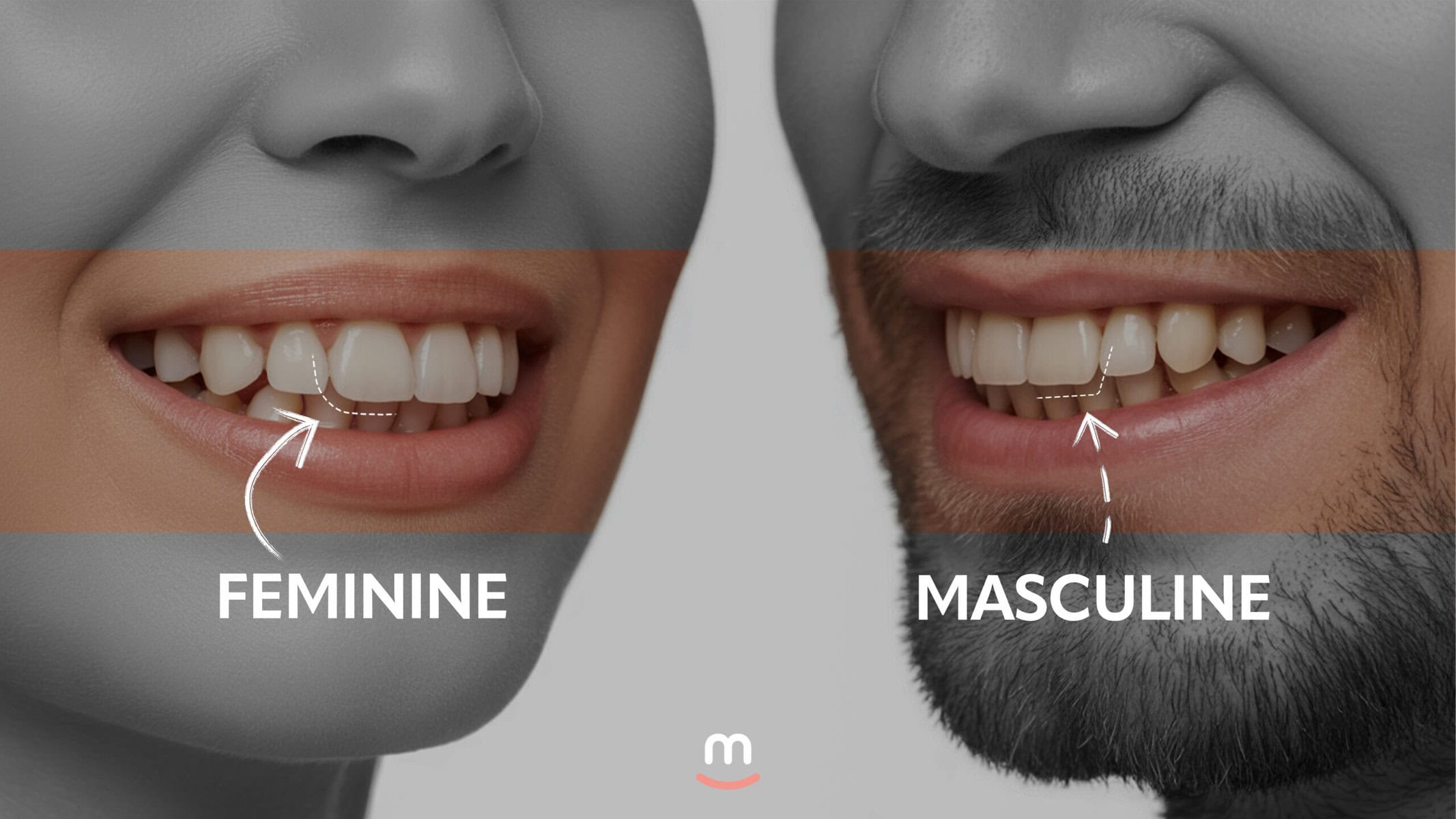
Feminine dental aesthetics emphasize softness, grace, and approachability, often characterized by smaller, more rounded tooth forms that convey youthfulness and warmth. Core features include oval or tapered central incisors with rounded distal angles and soft cervical transitions, creating a delicate appearance. The smile arc is typically convex, paralleling the lower lip's curvature for harmony, with 1.5-2mm of gingival display adding a subtle, inviting gum show that enhances femininity without excess. Minimal buccal corridors contribute to a narrower, more refined smile width, while distolingual rotation in lateral incisors imparts a playful, youthful vibe. These elements align with symmetrical, proportional teeth where the central incisors are slightly taller than the laterals, fostering an elegant dominance.
Color and translucency play pivotal roles in amplifying radiance. Softer shades like A1 or A2 on the Vita scale, with heightened incisal translucency, mimic natural light play for a pearly, glowing finish. High-gloss surfaces enhance this luminosity, evoking vitality and femininity. Lip dynamics further define the aesthetic: upward-curving commissures highlight embrasures between teeth, creating depth and allure, while a curved smile line with slight gum visibility promotes expressiveness. Rounded incisal edges, sometimes with subtle undulations or mamelons, soften the look, avoiding sharp angles for a more gentle profile.
Enhancements in aesthetic dentistry tailor these traits through minimally invasive procedures.
Feldspathic porcelain veneers, often 0.3-0.5mm thick with no-prep designs, allow rounded edges and satin glazes to emulate natural wear elegantly. Lithium disilicate veneers provide durability and high aesthetics for smile makeovers, correcting shape and color with predictability. Composite bonding offers a quick, cost-effective way to refine contours and close gaps, while teeth whitening brightens to softer hues. Gum contouring addresses excessive display for symmetry, and 3D-printed veneers enable precise, customized enhancements. These procedures focus on youthful, radiant outcomes, often incorporating digital smile design for previews.
Psychologically, feminine dental aesthetics tie deeply to self-perception and social interactions. An enhanced smile boosts confidence, equating to approachability and warmth, with studies linking attractive teeth to higher self-esteem and psychosocial well-being. Women often prioritize appearance in oral health, viewing it as integral to psychological adjustment and social competence. Ultimately, these features and enhancements empower personalized expressions of femininity, blending health with beauty.
Masculine dental aesthetics prioritize strength, ruggedness, and authority, featuring larger, squarer tooth forms that convey robustness and confidence. Core characteristics include square or semi-rectangular central incisors with pronounced line angles and reduced taper, creating a bold, angular profile. The smile arc is often flatter or inverted, contrasting the convex curve seen in feminine designs, with broader buccal corridors emphasizing width and power. Prominent canines add to the rugged look, while minimal gingival display typically 1mm or less, maintains a restrained, resolute expression. Lateral incisors align flatter with centrals, avoiding rotations for a straightforward, dominant arrangement. These traits align with broader male facial structures, such as square or triangular jaws, enhancing overall masculinity.
Color and translucency focus on a natural, robust vibe with higher value and lower chroma shades like B1 or B0.5, evoking a "power" aesthetic. Deeper perikymata and subtle surface textures mimic real wear, adding authenticity without excessive gloss. Lip dynamics involve lateral stretching for width emphasis, with a straighter smile line and flattened incisal edges suggesting durability. Pointed canines and minimal embrasures contribute to a commanding presence, often paired with broader arches for impact.
Enhancements in aesthetic dentistry aim for subtle, powerful transformations using minimally invasive techniques.
Monolithic lithium-disilicate veneers, 0.7-1.0mm thick with light chamfer preparations, provide crisp angles and durability for a masculine contour. Additive composite bonding refines shapes and closes gaps quickly, while teeth whitening achieves bold, white shades for vibrancy. Invisalign aligns teeth discreetly, and gum contouring minimizes excess display for a clean line. Digital smile design software previews masculine libraries, ensuring natural results that emulate wear facets for strength. These procedures favor efficiency, with veneers offering quick makeovers in a few visits.
Psychologically, masculine dental aesthetics are linked to leadership and self-assurance, with enhancements boosting psychosocial well-being and challenging stereotypes. Poor aesthetics can erode confidence, leading to social withdrawal, while improvements enhance self-esteem and professional perceptions. Men often seek treatments for youthful energy, redefining masculinity through subtle, empowering changes. Ultimately, these features and enhancements foster personalized expressions of strength, blending oral health with empowered identity.
Dental health profoundly impacts gender perceptions by intertwining physical well-being with aesthetic and psychological elements, where poor oral care can erode traits associated with femininity or masculinity.
Women typically demonstrate superior oral health behaviors, including more frequent brushing (odds ratio 1.95 times higher than men), flossing, and dental visits, reflecting higher oral health literacy and positive attitudes toward care. This diligence stems from a greater interest in oral hygiene and linking dental appearance to self-esteem, with women perceiving their oral health as integral to overall attractiveness and social competence. However, women are more susceptible to cavities, with higher prevalence due to hormonal fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, which increase gum sensitivity and plaque buildup. Conditions like TMJ disorders are also more common, potentially diminishing perceived femininity through pain or altered smiles.
In contrast, men exhibit poorer oral hygiene habits, fewer dental checkups, and worse self-perception of gum and tooth health, often influenced by masculinity norms that view seeking care as a sign of weakness or associate visits with pain. This leads to higher risks of gum disease 57% prevalence in men versus 39% in women, and oral cancer, exacerbated by lifestyle factors like smoking and alcohol. Such neglect can result in root caries, recession, and uneven wear, undermining masculine perceptions of strength and authority.
Behaviorally, women tie self-esteem more closely to oral health, with attractive smiles enhancing approachability and warmth, while men may experience social withdrawal from poor aesthetics, affecting leadership perceptions. Overall, suboptimal dental health erodes gender-aligned traits. Stained or decayed teeth may reduce feminine radiance, while gum issues can soften masculine ruggedness, highlighting the need for proactive, gender-aware care to boost confidence and perceptions.
Aesthetic dentistry has evolved to incorporate gender-specific considerations, ensuring procedures align with natural facial morphology and desired perceptions of softness for feminine smiles and strength for masculine ones. Common procedures include veneers, teeth whitening, composite bonding, gum contouring, dental crowns, orthodontics like Invisalign, and implants, often combined in smile makeovers for personalized results. These treatments address discoloration, misalignment, chips, gaps, and gum asymmetry, with digital smile design (DSD) software allowing previews of outcomes tailored to gender traits.
For feminine aesthetics, procedures emphasize delicacy and radiance.
These enhancements prioritize minimally invasive techniques, with recovery in 1-2 weeks, boosting self-esteem tied to warmth.
Masculine procedures, conversely, aim for boldness and ruggedness, breaking stereotypes by attracting more men to cosmetic care.
Key considerations include patient preferences over rigid stereotypes, integrating facial analysis for holistic results, and ensuring underlying health supports aesthetics. Costs vary ($500-$2,500 per tooth for veneers), but tailored approaches yield long-lasting confidence. Consult professionals to customize procedures for optimal gender-aligned enhancements.
Maintaining optimal dental health and appearance requires consistent habits tailored to individual needs, including gender-specific considerations, to preserve both functionality and aesthetics. Here are key tips to achieve brighter, healthier smiles:
By adopting these tailored tips, individuals can enhance confidence, align appearances with gender perceptions, and promote long-term oral health, ultimately leading to brighter, healthier smiles.
In exploring feminine appearance and masculine appearance in dental health, we've uncovered profound gender differences that shape not only anatomy but also aesthetics and well-being. Anatomically, men's larger, wider teeth contrast with women's smaller, narrower forms, influencing perceptions of rugged strength versus delicate softness. Aesthetically, feminine smiles feature rounded incisors, convex arcs, and radiant translucency for approachability, while masculine ones emphasize square shapes, flatter lines, and bold contours for authority. Health-wise, women's superior hygiene combats hormonal risks like cavities, whereas men's habits heighten gum disease prevalence, impacting gender-aligned traits.
Ultimately, prioritizing dental health empowers individuals to enhance confidence, self-expression, and social perceptions. Attractive smiles correlate with 20-30% higher self-esteem across genders. Whether seeking feminine dental enhancements like veneers for a glow or masculine procedures for robustness, personalized care from professionals ensures optimal results. Embrace these insights to achieve an optimized masculine or feminine smile that radiates health and vitality. Share this guide with others pursuing gender-specific oral aesthetics, or consult a dentist today for your tailored transformation. Your smile is your signature.
