Menu
Free Consultation
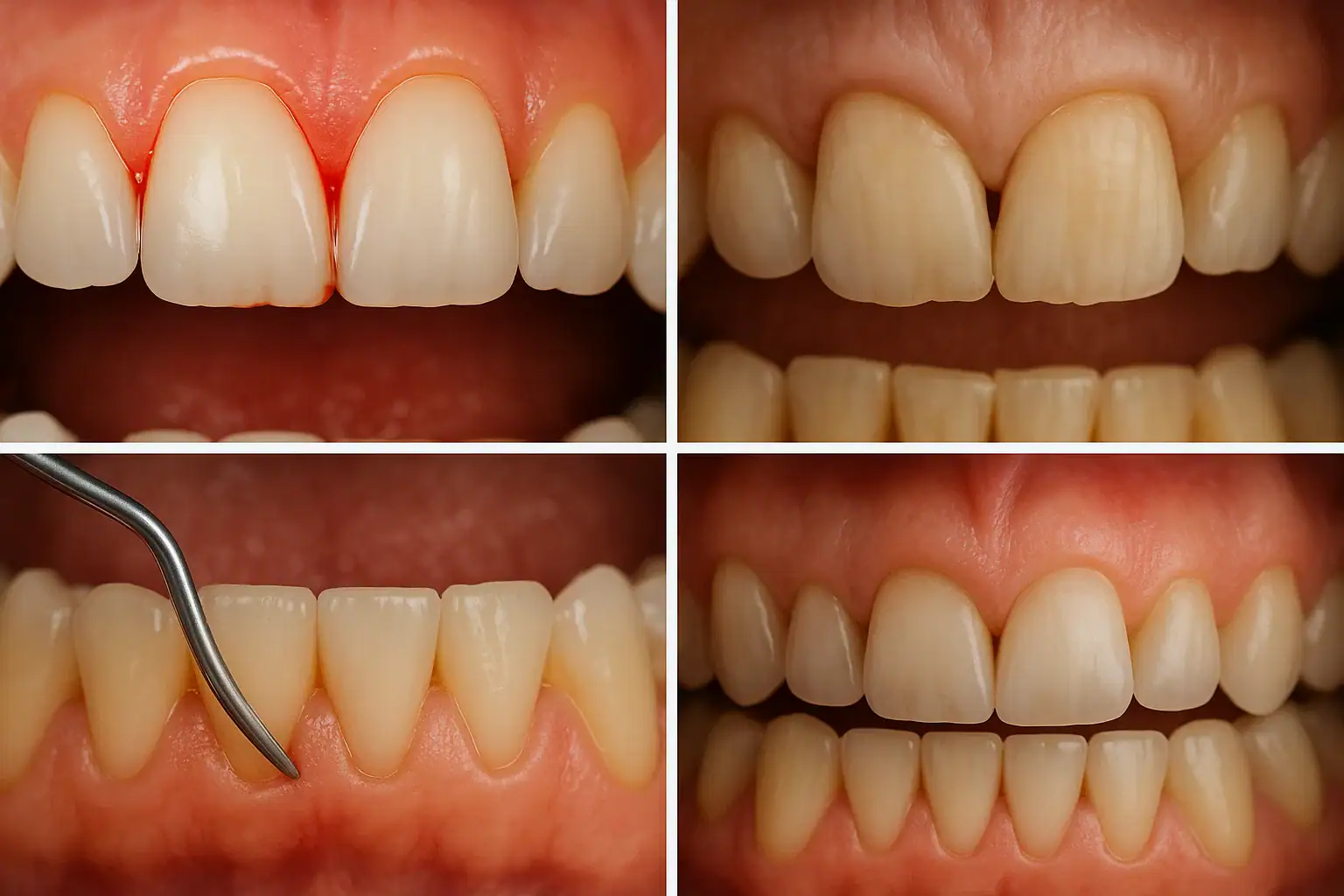
Gum bleeding and gum recession are among the most common yet most misunderstood oral health problems worldwide. Millions of people brush their teeth every day, use mouthwash regularly, and still wonder:
The truth is simple but often overlooked: healthy gums do not bleed, and gum recession is not just a cosmetic issue it is a biological warning sign.
This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about gum bleeding and gum recession, including causes, early warning signs, effective treatments, prevention strategies, and when professional care is essential.
Gum bleeding refers to bleeding from the gingival tissues, usually noticed during brushing, flossing, or sometimes even spontaneously. While many people assume it is normal, gum bleeding is always a sign of inflammation or disease.
No.
Healthy gums are firm, pink, and do not bleed. If bleeding occurs, it means the gums are inflamed and reacting to bacterial irritation.
The most common cause of gum bleeding is plaque accumulation along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky bacterial film that triggers inflammation. When plaque hardens into tartar, it becomes impossible to remove at home and continues to irritate the gums.
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease and is characterized by:
The good news: gingivitis is reversible with proper care.
If gingivitis is left untreated, it progresses into periodontitis. At this stage:
Periodontitis is a leading cause of adult tooth loss worldwide.
Brushing too hard, using a hard-bristled toothbrush, or brushing incorrectly can traumatize the gums, causing bleeding and recession.
Pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and hormonal fluctuations can increase gum sensitivity and bleeding.
Tobacco products reduce blood flow to the gums, mask symptoms, and accelerate gum disease progression.
This is one of the most searched dental questions globally.
Brushing daily does not guarantee gum health if:
In fact, inflamed gums bleed because bacteria are still present, not because you are brushing too much.
Gum recession occurs when gum tissue pulls away from the tooth, exposing the root surface. This condition develops gradually and is often painless until it becomes advanced.
Chronic inflammation destroys gum tissue and supporting bone.
Overbrushing is one of the most common non-disease-related causes of recession.
Some people are genetically predisposed to gum recession.
Excessive biting forces contribute to gum and bone loss.
Misaligned teeth place uneven pressure on gums.
This is one of the most important questions patients ask.
No, receding gums do not grow back naturally.
Once gum tissue is lost, the body cannot regenerate it on its own. However:
The foundation of all gum treatment. Removes plaque and tartar above and below the gumline.
A non-surgical periodontal treatment that cleans infected root surfaces and allows gums to heal.
Specialized rinses or localized treatments reduce harmful bacteria.
A surgical procedure that restores lost gum tissue and protects exposed roots.
Night guards or bite adjustment reduce damaging forces.
⚠️ These methods support treatment but do not replace professional care.
Many patients brush their teeth but completely ignore their gums.
Effective brushing must include:
Ignoring the gums allows bacteria to thrive exactly where disease begins.
You should seek professional care if:
Early intervention prevents irreversible damage.
Yes. It is often the first sign of gingivitis or periodontitis.
Early gum disease (gingivitis) can be reversed. Advanced disease requires professional treatment.
Flossing may cause temporary bleeding in inflamed gums, but it is necessary for healing.
No. Brushing harder worsens the condition.
Gum bleeding and gum recession are not minor problems—they are early warning signs of deeper oral and systemic health issues. Ignoring them allows disease to progress silently.
With proper diagnosis, professional treatment, and consistent home care, gum bleeding can be stopped and gum recession can be controlled.
Healthy gums mean:
If you are experiencing gum bleeding or recession, early professional evaluation is the most important step you can take.
